Ammonium sulfate
The basics of Ammonium Sulfate
Ammonium sulfate ((NH4)2SO4) is a product manufactured on a large scale and used mainly as a nitrogen fertilizer in agriculture. In addition, there are numerous other niche applications, e.g. as a food additive and in drinking water treatment.
(NH4)2 SO4 or AMSUL was one of the first and most widely used nitrogen (N) fertilizers for crop production. It’s now less common but especially valuable where both N and sulfur (S) are required. Its high solubility provides versatility for a number of agricultural applications.
Ammonium sulfate has been produced for more than 150 years. Initially, it was made from ammonia released during manufacturing coal gas (used to illuminate cities) or from coal coke used to produce steel. Today, manufacturers make it by reacting sulfuric acid with heated ammonia (see process schemes below).
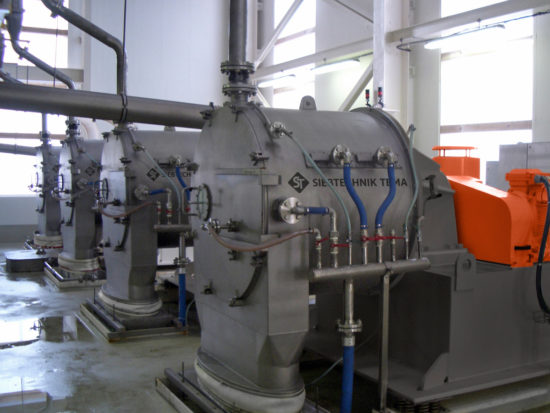
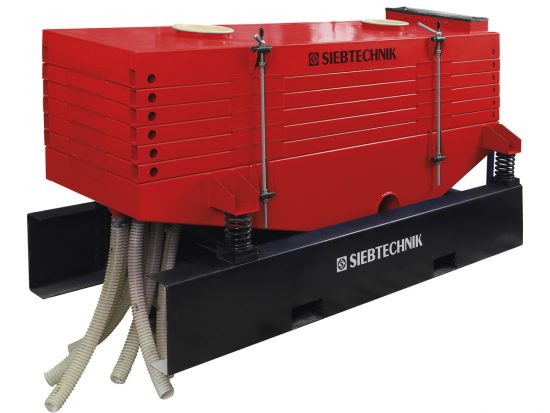
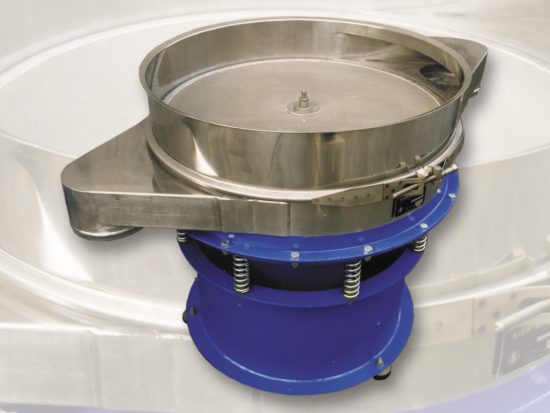
To get the crystal size best suited for the application, the reaction conditions are controlled by screening and drying (centrifuges & dryers) the particles until achieving the desired size. Some materials are coated with a conditioner to reduce dust and caking.
| SHS pusher centrifuge | CONTURBEX screen scroll centrifuge |
|---|---|
| 302 | 250 |
| 402 | 320 |
| 502 | 400 |
| 602 | 520 |
| 702 | 700 |
| 802 | 1000 |
| 1002 | 1200 |
| Typical machine sizes centrifuges | |

 Fertilizer – The primary use of Ammonium Sulfate is as a fertilizer for alkaline soils. In the soil the ammonium ion is released and forms a small amount of acid, lowering the pH balance of the soil, while contributing essential nitrogen for plant growth.
Fertilizer – The primary use of Ammonium Sulfate is as a fertilizer for alkaline soils. In the soil the ammonium ion is released and forms a small amount of acid, lowering the pH balance of the soil, while contributing essential nitrogen for plant growth.
 Food Additives | Acid Regulator (E517) – As a food additive, Ammonium Sulfate is considered generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and in the European Union it is designated by the E number E517. It is used as an acidity regulator in flours and breads.
Food Additives | Acid Regulator (E517) – As a food additive, Ammonium Sulfate is considered generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and in the European Union it is designated by the E number E517. It is used as an acidity regulator in flours and breads.
 Treatment of drinking water – In the treatment of drinking water, Ammonium Sulfate is used in combination with chlorine to generate monochloramine for disinfection.
Treatment of drinking water – In the treatment of drinking water, Ammonium Sulfate is used in combination with chlorine to generate monochloramine for disinfection.


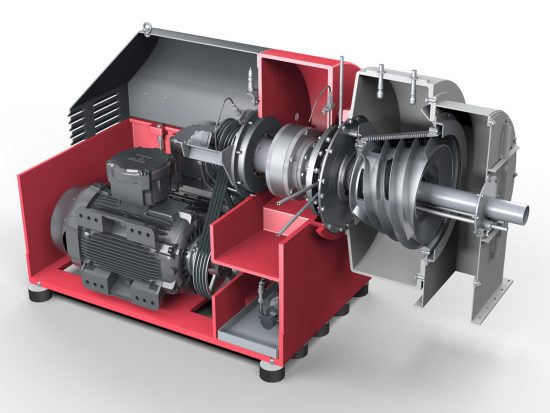
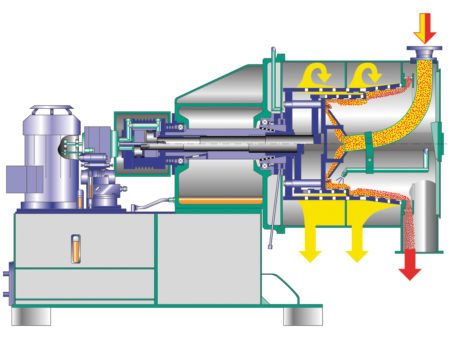
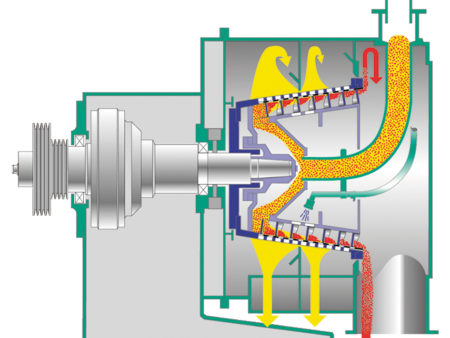
Ammonium Sulfate – Centrifuges
Selection Criteria for SHS & CONTURBEX
| SHS | CONTURBEX | |
|---|---|---|
 | 
| |
| Key factors | ||
| Solid concentration | Relatively constant feed conditions with solids concentrations starting at about 40%. | Very safe operation even with fluctuating solids concentrations due to forced solids transport. |
| Product washing | Highest product purities due to the long residence time of the product on the screen. | Good, but somewhat limited product purity due to shorter dwell time. |
| Solid throughput / yield | Smooth product transport, large solid cake height - and consequently less particle breakage - reduce solids losses to the filtrate and increase the yield. | Thinner solids layer provides rapid dewatering, but may result in more particle breakage and higher solids losses. Application often in the separation of fine ammonium sulfate crystals. |
| Residual moisture | Optimal dewatering of the crystals even at lower G-force and after a product wash due to long residence time on the screen. | Higher G-force ensures fast and optimal dewatering even with finer crystals. |
| Cleaning | The product remains in the screening drum after the feed stop. Unloading of the machine before restart by automated cleaning. | Self-cleaning effect due to the scroll - minimal residual amount of product remains in the screening drum after the feed stop. Machine can be cleaned even after a restart. |
| Sealing system | Vapour- and gas tight execution available. | Vapour- and gas tight execution available. |
Ammonium Sulfate Processes
Ammonium sulfate – recovering from wastewater
A) Recovering ammonium sulfate from sulfuric- or ammonia containing wastewater from processes such as:
- Caprolactam (CPL)
→ Polyamide 6 (textile fiber, foil) - Acrylnitrile (AN)
→ Acrylamide, glue, solvents - Methylmethacrylate (MMA)
→ Acrylic glass (plexiglass).
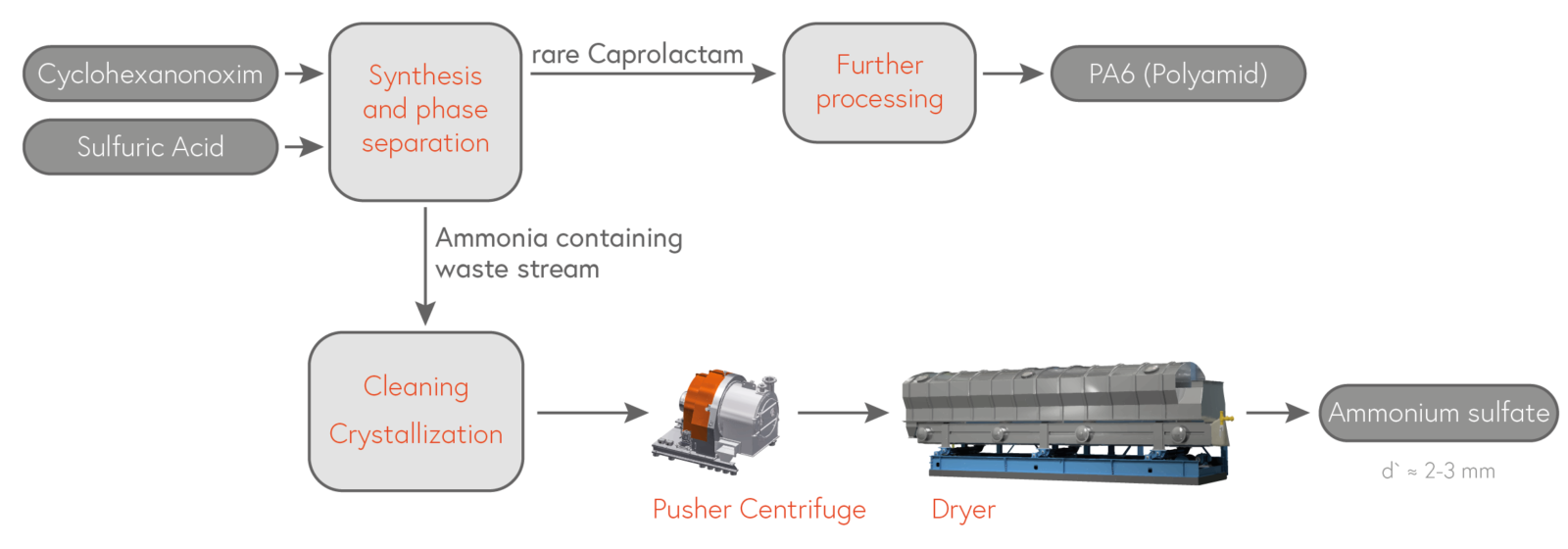
In industrial terms, ammonium sulfate is produced as a by-product in some chemical processes, especially in the production of caprolactam. Coarse-grained products (in the range of 2 to 4 mm) can be produced from such ammonium sulfate-containing wastewater in so-called DTB (Draft Tube Baffle) or Oslo crystallizers. This is important to ensure good spreadability when applying the fertilizer to the fields.
Ammonium sulfate out of ammonia gas and sulfuric acid
B) Synthetic production of ammonium sulfate out of ammonia gas and sulfuric acid.
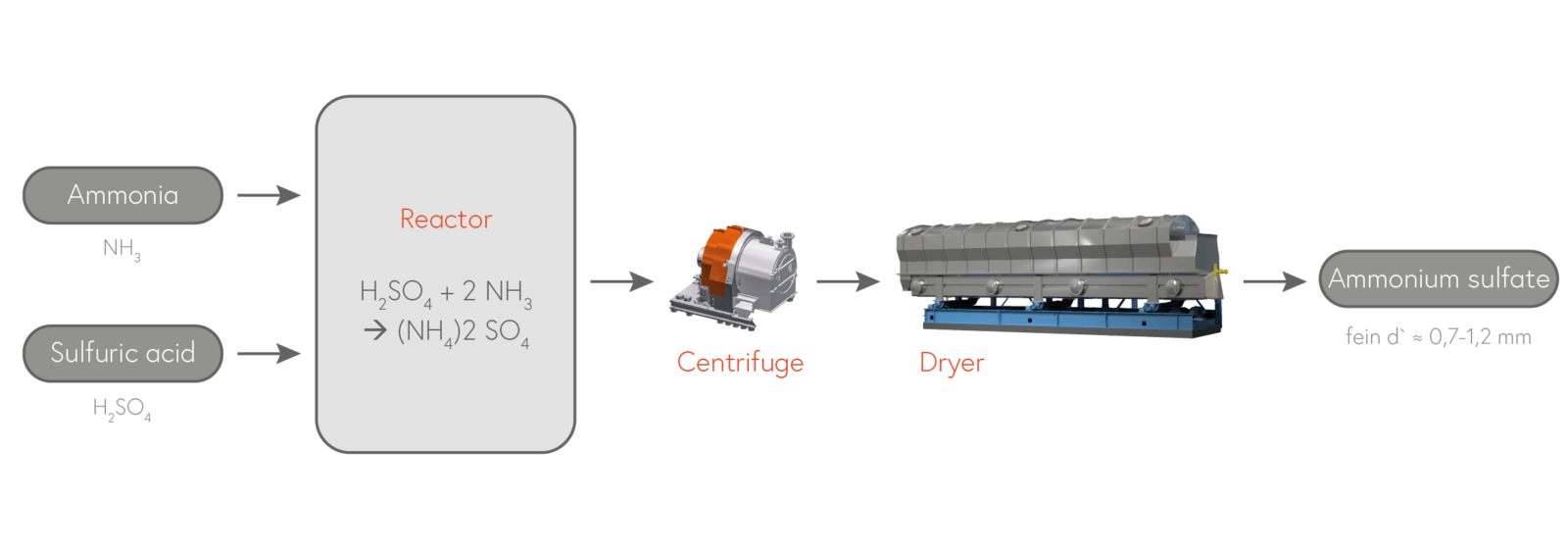
Synthetically, ammonium sulfate is obtained by reacting gaseous ammonia and sulfuric acid. In this application, too, the processing of „waste sulfuric acid“ from production processes is more the reason for building ammonium sulfate plants than the global demand for ammonium sulfate. Due to unavoidable dissipative processes during the fast reaction, the product from reaction crystallizers is significantly finer and therefore cheaper than the higher quality product from DTB crystallizers.
Ammonium sulfate as by-product (desulfurization)
C) By-product of the desulfurization of coke oven gas.
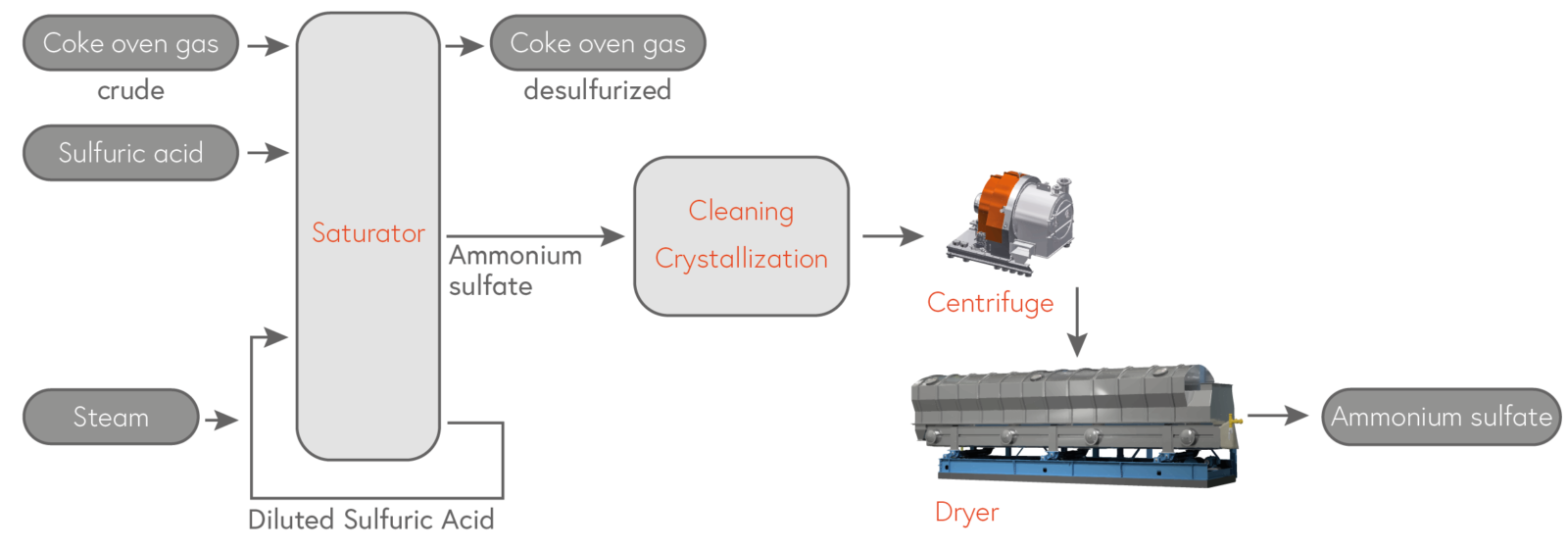
A comparable process for avoiding sulfur waste is also used in the purification of coke oven gas. Flue gas desulfurization produces ammonium sulfate as a byproduct.